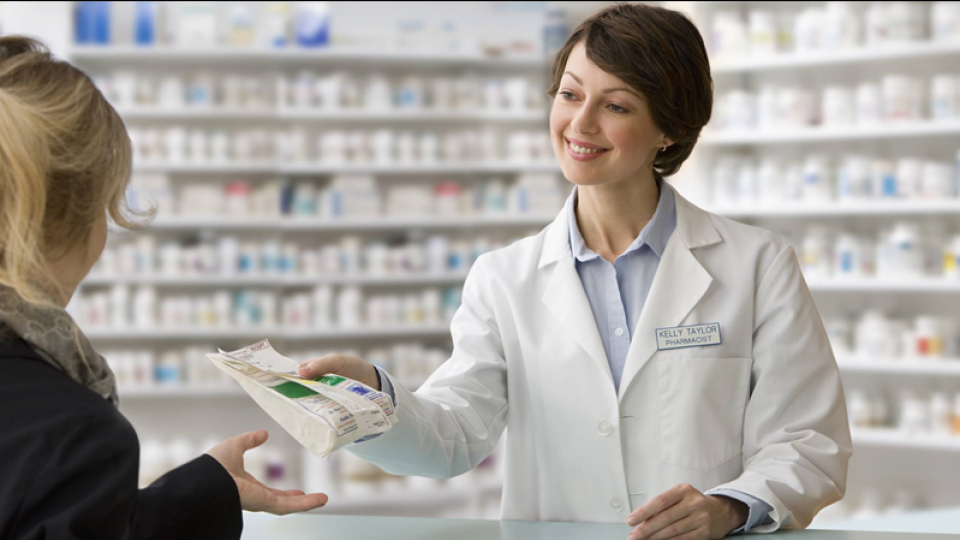
Pharmacists are essential members of the healthcare system, contributing significantly to patient well-being and the effective use of medications. They are often the most accessible healthcare professionals, providing crucial support not only through medication management but also through health education and patient care. The role of pharmacists extends beyond dispensing medications; they are involved in monitoring patient health, ensuring safe medication practices, and offering guidance on a range of health issues. As healthcare continues to evolve, pharmacists adapt to meet new challenges, making their role increasingly important in promoting public health and enhancing the quality of care.
What is a Pharmacist?
Definition and Role of a Pharmacist
A pharmacist is a licensed healthcare professional who specializes in the preparation, dispensation, and proper use of medications. They work to ensure that patients receive the correct medication and understand how to use it safely and effectively. Pharmacists are trained to provide expert advice on drug interactions, side effects, and proper dosages. Their role also includes reviewing prescriptions for accuracy, ensuring medications are administered correctly, and offering patient counseling. Pharmacists collaborate with doctors, nurses, and other healthcare providers to optimize patient care and improve health outcomes.
Different Types of Pharmacists
Pharmacists work in various settings, each requiring specific expertise. Community pharmacists operate in retail pharmacies and are the most visible to the public, providing medication and health advice. Hospital pharmacists work within healthcare facilities, focusing on inpatient medication management and working closely with medical teams. Clinical pharmacists specialize in direct patient care, often in specialty areas like oncology or cardiology. Additionally, some pharmacists engage in research, education, or regulatory roles, contributing to advancements in the field and improving healthcare practices.
Education and Training for Pharmacists
Educational Requirements
Becoming a pharmacist requires extensive education and training. Aspiring pharmacists typically need to complete a Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D.) program, which usually takes four years of professional study following undergraduate coursework. The Pharm.D. program covers subjects like pharmacology, medicinal chemistry, and patient care. Additionally, prospective pharmacists must pass national and state licensing exams to practice legally. This rigorous educational path ensures that pharmacists have the knowledge and skills necessary to perform their roles effectively.
Key Skills and Training Involved
Pharmacists need a blend of technical and interpersonal skills. They must be adept at understanding complex medication regimens and diagnosing potential drug interactions. Strong communication skills are crucial, as pharmacists often explain medication instructions to patients and collaborate with other healthcare professionals. Training includes practical experience through internships or residencies, where students apply their knowledge in real-world settings. Continuous professional development is also important, as pharmacists must stay updated with the latest medical advancements and changes in drug therapies.
Daily Responsibilities of Pharmacists
Common Tasks Performed by Pharmacists
On a daily basis, pharmacists handle a variety of tasks. They review and process prescription orders, ensuring accuracy and appropriateness. Pharmacists also provide counseling to patients on how to take their medications, including dosage instructions and potential side effects. They manage inventory, including ordering and stocking medications, and may perform administrative duties related to patient records and insurance claims. In addition, pharmacists often conduct health screenings and provide immunizations, playing a proactive role in disease prevention and health promotion.
Examples of Their Daily Work
Pharmacists’ daily work involves more than just filling prescriptions. They may consult with physicians to adjust medication therapies based on a patient’s specific needs or health conditions. For example, if a patient is experiencing adverse effects from a medication, a pharmacist might suggest an alternative or a dosage adjustment. They also handle medication therapy management (MTM), which includes reviewing a patient’s entire medication regimen to ensure safety and efficacy. Additionally, pharmacists provide educational materials and advice to patients, helping them understand their health conditions and treatment options.
Pharmacists’ Role in Patient Care
How Pharmacists Contribute to Patient Health
Pharmacists play a pivotal role in patient health by ensuring the safe and effective use of medications. They help patients manage chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and asthma through medication management and lifestyle advice. By conducting medication reviews, pharmacists can identify and resolve issues such as drug interactions, duplications, or allergies. They also support disease prevention through vaccinations and health screenings. Their role extends to providing emergency care, such as administering first aid or managing medication-related emergencies.
Examples of Patient Care Responsibilities
Pharmacists’ patient care responsibilities are diverse. For instance, in a hospital setting, a pharmacist may be involved in developing and monitoring individualized treatment plans for patients with complex medical conditions. In a community pharmacy, they might offer diabetes education programs, helping patients understand how to monitor their blood sugar levels and use insulin correctly. Pharmacists also provide support for medication adherence, assisting patients in overcoming barriers to following their prescribed treatments and improving their overall health outcomes.
Pharmacists and Medication Management
The Importance of Medication Management
Medication management is a critical aspect of pharmacy practice. Proper management ensures that medications are used effectively and safely, minimizing risks and enhancing therapeutic outcomes. Pharmacists review medication regimens to prevent errors, manage potential drug interactions, and adjust dosages as needed. Effective medication management helps prevent adverse effects, reduces hospitalizations, and improves patient compliance with treatment plans. By providing thorough medication counseling and monitoring, pharmacists contribute significantly to the overall quality of patient care.
How Pharmacists Help with Prescriptions and Over-the-Counter Drugs
Pharmacists assist with both prescription and over-the-counter (OTC) medications. For prescriptions, they verify the accuracy of the medication, provide guidance on how and when to take it, and monitor for potential side effects or interactions with other drugs. For OTC medications, pharmacists offer advice on suitable products for common ailments, such as coughs, colds, and pain. They also educate patients on proper use and possible side effects of OTC drugs, ensuring safe and effective self-medication.
Pharmacists in Different Settings
Community Pharmacies
Community pharmacies are perhaps the most familiar setting for pharmacists. In these environments, pharmacists provide essential services such as dispensing medications, offering health advice, and conducting wellness screenings. They often serve as the first point of contact for patients seeking healthcare information. Community pharmacists also play a key role in preventive care, including immunizations and health education, and in managing minor health issues that don’t require a doctor’s visit.
Hospitals and Clinics
In hospitals and clinics, pharmacists work as part of the healthcare team to manage and optimize medication use for inpatients. They review and approve medication orders, monitor patient responses, and collaborate with doctors and nurses to adjust therapies. Hospital pharmacists also provide specialized services, such as chemotherapy preparation and clinical trials. Their role is critical in ensuring that patients receive safe and effective medication therapies during their hospital stay.
Research and Academia
Some pharmacists work in research or academic settings, contributing to the advancement of pharmaceutical sciences. In research roles, they investigate new medications, treatment protocols, and drug interactions, aiming to improve therapeutic options. Academic pharmacists teach future pharmacists and engage in scholarly activities, helping to advance the field of pharmacy through education and research. Their work supports the development of new therapies and enhances the understanding of existing ones.
Challenges Faced by Pharmacists
Common Issues and Challenges in the Profession
Pharmacists face several challenges in their profession. One major issue is the increasing workload, which can lead to stress and burnout. Pharmacists must manage a high volume of prescriptions and patient interactions, often with limited time. Additionally, staying current with rapidly evolving medical knowledge and drug therapies requires continuous learning. Pharmacists also face challenges related to reimbursement and insurance policies, which can affect their ability to provide optimal care.
Strategies to Overcome These Challenges
To overcome these challenges, pharmacists can employ various strategies. Effective time management and organizational skills help manage workloads and reduce stress. Continuing education and professional development keep pharmacists updated on the latest advancements in the field. Advocating for improved working conditions and seeking support from professional organizations can also address issues related to reimbursement and policy. Collaboration with healthcare teams and leveraging technology can enhance efficiency and patient care.
The Future of Pharmacy
Emerging Trends and Advancements
The field of pharmacy is evolving with advancements in technology and changes in healthcare delivery. Emerging trends include the use of digital health tools, such as electronic health records and telepharmacy, which enhance patient care and streamline medication management. Personalized medicine, which tailors treatments based on individual genetic profiles, is another exciting development. Pharmacists are increasingly involved in managing complex therapies and coordinating care across different healthcare providers, reflecting a broader and more integrated role in patient health.
How the Role of Pharmacists Might Change
The role of pharmacists is expected to continue evolving. As healthcare systems emphasize patient-centered care and interdisciplinary collaboration, pharmacists will take on more responsibilities in direct patient care and health management. They may play a greater role in preventive care, chronic disease management, and medication therapy management. Advances in technology and data analytics will enable pharmacists to provide more personalized and efficient care, further integrating their role into the healthcare team and enhancing their impact on patient health.
Conclusion
Pharmacists are indispensable to the healthcare system, playing a vital role in medication management, patient care, and health promotion. Their expertise ensures that medications are used safely and effectively, contributing to better health outcomes and quality of life for patients. Understanding and appreciating the diverse roles of pharmacists helps highlight their significance in healthcare and underscores the value they bring to patients and the broader health system. As the field of pharmacy continues to advance, pharmacists will remain at the forefront of improving patient care and advancing public health.